
RESEARCH The essential role of redox regulation in health and disease is undisputed. Redox reactions – electron transfer reactions – are required for almost all aspects of a cell´s life. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have long been considered to be exclusively deleterious by damaging DNA, proteins, and lipids. Meanwhile, ROS were uncovered as important second messengers for specific signaling events via reversible oxidative posttranslational thiol modifications. Adequate reaction velocity and appropriate specificity for regulation of these modifications is mediated by enzymes, especially by oxidoreductases of the thioredoxin family, namely thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, and peroxiredoxins. In our former work we identified members of this protein family as Fe2S2 cluster coordinating enzymes and important roles during iron metabolism of some of those. We also revealed essential functions of a specific glutaredoxin during vertebrate development of the cardiovascular system and the brain. 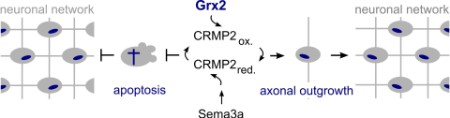
Glutaredoxin 2 (Grx2) is essential for embryonic development of a functioning brain via redox regulation of collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2). Our current work is embedded in the research activities of the Department of Neurology, Heinrich-Heine University Düsseldorf (headed by S. Meuth). We aim at the translation of our former findings regarding redox regulation and iron metabolism as well as the redox- and iron-dependent cell death mechanism ferroptosis as a crosstalk of both into the medical context of neurological deficits, focusing on neuroinflammation, e.g. multiple sclerosis. 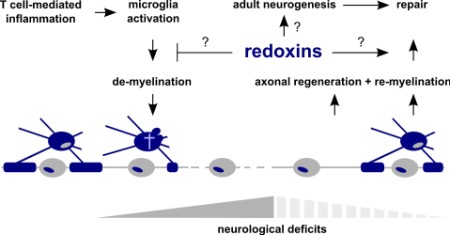
Schematic overview of our current research: grey cells: neurons, blue cells: oligodendrocytes, redoxins: thio- and glutaredoxins. In general, we investigate specific thiol redox events (Thiology) affecting metabolic processes and signaling cascades in cytosol, mitochondria, and nucleus underlying physiological cellular processes, disease progression, and regeneration of damaged tissue. most recent reviews: - Berndt C, Christ, L, Rouhier, N, and Mühlenhoff, U,Glutaredoxins with Iron-Sulfur-Clusters -Structure, Function and impact on Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Bioenergetics 1882: 148317 (2021)
- Wolf, C, del Amo, VL, Arndt, S, Bueno, D, Tenzer, S, Hanschmann, EM, Berndt C, Methner, A, Redox Modifications of Proteins of the Mitochondrial Fusion and Fission Machinery. Cells 9: 815 (2020)
- Berndt, C, Lillig, CH, Glutathione, Glutaredoxins, and Iron. Antioxid Redox Signal 27: 1235-1251 (2017)
- Sies H, Berndt C, Jones DP, Oxidative stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 86: 715-748 (2017)
Lepka K, Berndt C, Hartung HP, Aktas O, Redox events as modulators of pathology and therapy of neuroinflammatory diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 4: 63 (2016) - Berndt C, Lillig CH, Flohé L, Redox regulation by glutathione needs enzymes. Front Pharmacol 5: 168 (2014)
All publications are listed here. press releases / press articles For financial support of our former and present research we thank:  
|

